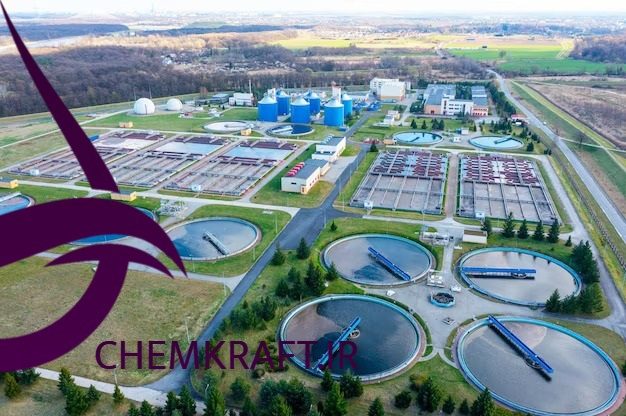
Main wastewater treatment chemicals play a crucial role in the removal of impurities and toxins from wastewater, ensuring its safe disposal or reuse. These chemicals are added during the treatment process to enhance the efficiency of various treatment methods. The effectiveness of these chemicals is dependent on factors such as the nature and concentration of contaminants, as well as the desired end result of the treatment process.
Chemicals Industries
Caustic soda, also known as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), is a versatile chemical compound that plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. From household cleaning products to industrial processes, caustic soda has a wide range of applications that make it indispensable in various sectors.
Main ion exchange membrane producers of the world play a crucial role in providing high-quality and efficient membranes for various applications. These producers utilize advanced technologies and manufacturing processes to produce membranes that meet the growing demands of industries such as energy, water treatment, and chemical processing. In this essay, we will explore some of the leading ion exchange membrane producers in the world.
Definition
Caustic soda, also known as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), is an essential chemical compound used in various industrial processes. It is a strong base and highly reactive, making it a key ingredient in the production of various products like paper, soap, and detergents. This essay will describe the process involved in the production of caustic soda.
Introduction to Caustic Soda
Caustic soda, also known as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), is a highly versatile compound that finds numerous applications across various industries. It is a strong alkaline chemical that is widely used in chemical manufacturing, water treatment, textile and paper production, food processing, metallurgy, and soap manufacturing, among others. Caustic soda plays a crucial role in these industries due to its ability to react with acids, regulate pH levels, and perform various chemical and cleaning processes. This article delves into the diverse applications of caustic soda in different sectors, highlighting its significance and impact within each industry.
Introduction to Caustic Soda and its Hazards
Caustic soda hazards: Caustic soda, also known as sodium hydroxide, is a highly corrosive chemical commonly used in various industrial applications. From manufacturing to water treatment, caustic soda plays a vital role. However, handling this substance requires utmost caution due to its hazardous nature. This article aims to provide essential safety precautions for the proper handling of caustic soda, whether in flake or liquid form. By understanding the potential risks associated with caustic soda and implementing appropriate safety measures, individuals and organizations can ensure the well-being of personnel, prevent accidents, and maintain a safe working environment.
Ammonium Bifluoride (ABF)
Ammonium bifluoride (ABF) is a compound with various industrial applications, known for its versatile chemical properties. With the formula NH4HF2, ABF is commonly used as a source of fluoride ions and in the preparation of other fluorine-containing compounds. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of ABF, exploring its chemical properties, production process, raw materials, purification techniques, and quality control measures. Furthermore, it will delve into the wide range of applications where ABF finds utility, while also addressing safety considerations associated with handling this compound. By delving into the formula and production process of Ammonium bifluoride, this article aims to shed light on this important chemical compound and its significance in various industries.
Introduction
Ammonium bifluoride (ABF) is a versatile compound that finds numerous applications in various industries due to its unique chemical properties. This essay aims to explore the multifaceted applications of ABF, emphasizing its role in analytical chemistry, metal surface treatment, glass etching, nuclear power, and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
AMPS Copolymer application in textile
AMPS Copolymer application in textile industry has seen immense growth and development over the years. With a wide range of fabrics available in the market, manufacturers are constantly looking for ways to enhance the quality and durability of their products. One such method is the utilization of AA/AMPS as dyeing auxiliaries in textile production. This essay will discuss the importance and efficacy of AA/AMPS in the dyeing process, highlighting its various applications and benefits.
AAA/AMPS Copolymer – A High-Performance Polymer for Various Industries
What is AAA/AMPS Copolymer?
Manufacturers create the AAA/AMPS copolymer by combining Acrylic Acid (AAA) with 2-Acrylamido-2-Methylpropane Sulfonic Acid (AMPS). This copolymer offers high water solubility, superior thermal stability, and excellent dispersing properties, making it essential for various industrial applications. Industries such as water treatment, oil & gas, textiles, and cleaning products widely use it to prevent scaling, control fluid viscosity, and improve detergent formulations..