Coagulant DST454
Coagulant DST454 Another type of coagulants are cationic polymers. Unlike inorganic coagulants such as alum and iron chloride, cationic polymers are organic compounds.
They exhibit strong positive charges and work by binding negatively charged particles suspended in liquid.
Cationic polymers are often used in wastewater treatment and sludge dewatering processes.
They are effective in destabilizing and agglomerating fine particles that are not easily removed by traditional coagulants.
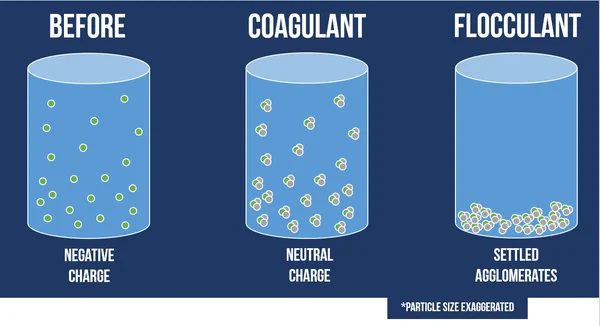
Coagulants are chemical compounds that enhance the coagulation process. They work by destabilizing suspended particles in a liquid, causing them to aggregate and form larger organisms. This phenomenon is significant in water treatment, where coagulants are used to remove impurities, such as suspended solids and pathogens, from contaminated water sources. By binding to these contaminants, coagulants form solid masses that can be easily separated from water through sedimentation or filtration methods.