Definition
Ammonium fluosilicate is a chemical compound that is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties and versatility. Its chemical formula is (NH4)2SiF6, and it is also known as ammonium hexafluorosilicate. In this essay, we will explore the analysis, formula, and applications of ammonium fluosilicate.
Analysis
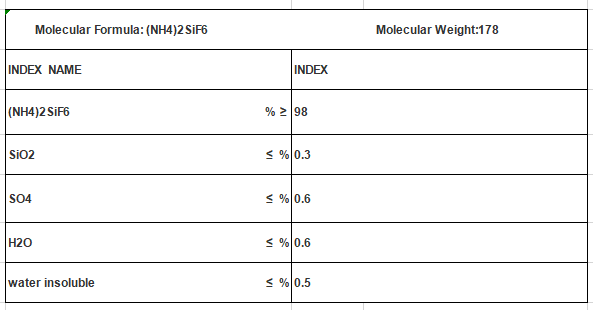
Ammonium Fluosilicate CAS NO 16919-19-0 (NH4)2SiF6
Molecular Formula: (NH4)2SiF6
Mol. Wt: 178
Cas No.: 16919-19-0
UN No.: 2854
EMS No.: F-A, S-A
EINECS: 240-968-3
Analyzing ammonium fluosilicate involves various techniques to determine its composition and purity. One common method is spectroscopy, such as infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which can identify the chemical bonds and molecular structure. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) are commonly employed to determine the crystal structure and elemental composition, respectively. Additionally, elemental analysis techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) can quantify the concentration of different elements in the compound. These analytical techniques ensure that it meets the desired specifications for specific applications.
The chemical formula for it provides valuable insight into its composition. It consists of two ammonium ions (NH4+) and one hexafluorosilicate ion (SiF6^2-). The ammonium ion is made up of one nitrogen atom and four hydrogen atoms, while the hexafluorosilicate ion consists of one silicon atom and six fluorine atoms. The presence of fluorine makes ammonium fluosilicate highly reactive and gives it unique properties.
Applications
Ammonium fluosilicate has a wide range of applications across different industries. It is commonly used as a fluorine source in the glass industry, where it acts as a flux during the glass melting process. The addition of this compound to the glass batch reduces the melting point and viscosity, facilitating the shaping and forming of glass products. In the metallurgical industry, it is used as a component of fluxes to lower the melting point of metal oxides during the extraction and refining of metals. Additionally, ammonium fluosilicate finds application as an etching agent in the electronic industry to selectively remove oxide layers from silicon wafers.
Another significant application of this chemical is in the preparation of pesticides. It is used as an active ingredient in insecticides due to its potent insecticidal properties. Its ability to disrupt insect nervous systems and damage insect cells makes it an effective pesticide. Furthermore, ammonium fluosilicate is employed in water treatment as a coagulant and flocculant. It helps in the removal of unwanted particles, ions, and impurities from water, ensuring its purity and safety for consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ammonium fluosilicate, with its (NH4)2SiF6 chemical formula, is an essential compound with various applications in multiple industries. Its analysis involves techniques like spectroscopy and elemental analysis to ensure its purity and composition. The addition of this compound as a flux in the glass and metallurgical industries assists in reducing melting points and viscosity, facilitating manufacturing processes. Insecticides, water treatment, and etching agents are among other important applications of this compound. The versatile nature of it makes it a valuable chemical compound in numerous industrial applications.
Ammonium Fluosilicate (NH4SiF6): A Multifaceted Compound in Various Industries
Ammonium Fluosilicate, also known as NH4SiF6, is a versatile chemical compound that finds application across diverse industries due to its unique properties and reactivity. This essay delves into the extensive applications of NH4SiF6, emphasizing its significance and impact on different sectors.
Introduction:
NH4SiF6 is derived through the reaction between silicon dioxide (SiO2) and hydrofluoric acid (HF), resulting in a compound notable for its stability and solubility in water. This essay explores the broad spectrum of applications of Ammonium Fluosilicate, highlighting its role in various industrial processes.
Metal Surface Treatment and Anodizing:
NH4SiF6 is a key player in metal surface treatment, particularly in the preparation of aluminum surfaces for anodizing. As an etchant, it removes impurities and oxides, ensuring enhanced adhesion and uniform anodized coatings. This application is pivotal in industries such as aerospace, providing improved corrosion resistance and durability.
Electroplating Enhancement:
In electroplating processes, NH4SiF6 serves as an electrolyte, contributing to smoother and more uniform metal deposition. This enhancement is critical for industries like electronics and automotive, where high-quality coated products are essential for performance and longevity.
Catalyst in Organic Synthesis:
The catalytic properties of NH4SiF6 make it invaluable in organic synthesis reactions. Acting as a Lewis acid catalyst, it activates substrates, facilitating efficient and selective reactions. This catalytic role is crucial in the production of pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, and polymers, enhancing overall synthetic processes.
Glass Etching Expertise:
NH4SiF6 is employed in the glass industry as an etching agent. Its ability to selectively remove thin layers of glass enables the creation of intricate designs in decorative glassware, glass art, and electronic components. This controlled etching process is vital for achieving precise and aesthetically pleasing results.
Concrete and Cement Additive:
In the construction industry, NH4SiF6 serves as an additive in the production of concrete and cement. Its reaction with alkaline compounds in cement contributes to the development of long-lasting and resilient infrastructure. This application enhances the strength and durability of concrete structures, ensuring their longevity.
Uranium Extraction and Nuclear Industry:
NH4SiF6 plays a crucial role in the nuclear industry, particularly in the extraction and purification of uranium. The compound reacts with uranium compounds, forming soluble complexes. This process is fundamental for the production of nuclear fuel, contributing significantly to the generation of nuclear energy.
Fluoride Production for Water Treatment:
A notable application of NH4SiF6 lies in water fluoridation. Its controlled addition to water supplies helps prevent tooth decay and promotes dental health by maintaining a consistent fluoride concentration. This widely adopted practice contributes to public health on a global scale.
Controlling Organizations and Safety:
Regulations and guidelines for the use of NH4SiF6 and other fluorine compounds are overseen by various international, national, and regional bodies. A significant organization in this regard is the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA), collaborating to ensure responsible chemical use and safety.
For specific regulations, individuals and organizations can refer to bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe. These agencies provide comprehensive information on the safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals, aligning with safety and environmental standards.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Ammonium Fluosilicate (NH4SiF6) stands as a compound with diverse applications across various industries. From metal surface treatment and electroplating to catalysis in organic synthesis and water fluoridation, NH4SiF6 plays a significant role in enhancing industrial processes. The existence of controlling organizations ensures responsible use, contributing to safety and environmental standards in the chemical industry. As research and development continue, NH4SiF6 may reveal new applications, further establishing its significance in chemical processes and industrial applications.


