Definition
Fluoroboric acid, also known as tetrafluoroboric acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HBF4. It is a strong acid and one of the most important fluorine-containing compounds. This essay will provide an analysis of fluoroboric acid, discussing its formula, properties, applications, and safety precautions.
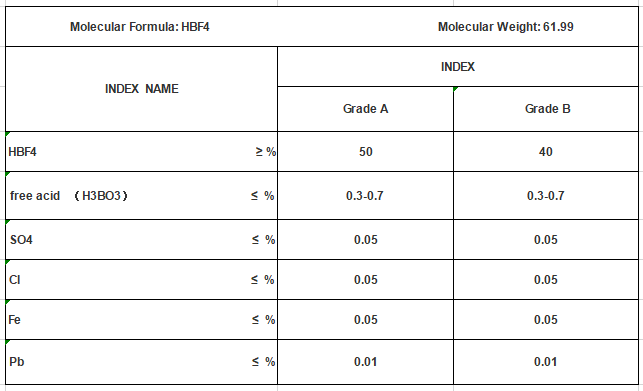
The formula of fluoroboric acid, HBF4, indicates that it contains one hydrogen atom (H) and one boron atom (B), both of which are bonded to four fluorine atoms (F). This compound is highly corrosive and has a low viscosity, making it a liquid at room temperature. It is soluble in water and various organic solvents, allowing for various applications in both industrial and laboratory settings.
Applications
The unique properties of fluoroboric acid make it highly versatile and useful in several applications. One of its primary uses is as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. Due to its high acidity, it can facilitate reactions by acting as a proton donor. It is also employed in electroplating processes, where it acts as an electrolyte to produce a thin layer of metal on a surface. Furthermore, this acid is used as a flux in soldering, as it improves the flow of molten solder and enhances the wetting properties on the surfaces to be soldered.
Safety
As with any strong acid, it is essential to handle and use fluoroboric acid with caution. It can cause severe burns and is toxic if inhaled or ingested. Therefore, it is crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat, when working with this compound. It is also essential to store fluoroboric acid in a well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials, such as strong bases or reducing agents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this acid, with the chemical formula HBF4, is a strong acid used in various chemical reactions, electroplating processes, and soldering. Its high acidity and unique properties make it a valuable catalyst and electrolyte. However, due to its corrosive nature, it must be handled with caution and proper safety precautions. As researchers continue to explore its properties and applications, fluoroboric acid will likely continue to play a significant role in various scientific and industrial fields.
Title: Fluoroboric Acid Applications: Versatility in Industry
Fluoroboric Acid, commonly known as tetrafluoroboric acid, exhibits a wide array of applications across industries, owing to its unique properties and reactivity.
Electroplating and Surface Treatment: Utilized as an electrolyte in electroplating, Fluoroboric Acid enhances efficiency, yielding uniform metal coatings in various industries.
Organic Synthesis Catalyst: Functioning as a Lewis acid catalyst, it aids in efficient organic synthesis, enabling the production of pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals.
Laboratory Reagent and Research: In laboratories, Fluoroboric Acid serves as a versatile reagent, contributing to chemical analyses and experimental procedures.
Battery Electrolyte: As an electrolyte in batteries, including lead-acid batteries, this chemical impacts energy storage and renewable energy systems.
Electronics Etching Agent: In electronics, Fluoroboric Acid’s role as an etching agent facilitates precise patterning for integrated circuits and microelectronics.
Controlling Organizations: Regulation of fluorine compounds, including Fluoroboric Acid, is overseen by various bodies. The International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) collaborates for responsible chemical use.
Specific regulations depend on the region. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. and European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe enforce standards.
In conclusion, Fluoroboric Acid’s applications, from electroplating to electronics, highlight its versatility. Regulatory bodies ensure responsible use, aligning with safety and environmental standards.



