Definition
Ammonium Fluorozirconate (NH4ZrF6) is a white crystalline solid compound that is commonly used in various industries due to its unique properties. In this essay, we will explore the analysis, formula, and applications of it.
To analyze Ammonium Fluorozirconate, several techniques can be used. One common method is X-ray diffraction, which allows for the determination of the crystal structure of the compound. This technique uses the scattering of X-rays by the crystalline material to study the arrangement of atoms within the compound. Additionally, spectroscopic techniques such as infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify the functional groups present in Ammonium Fluorozirconate. These analytical techniques provide valuable insights into the composition and structure of this compound.
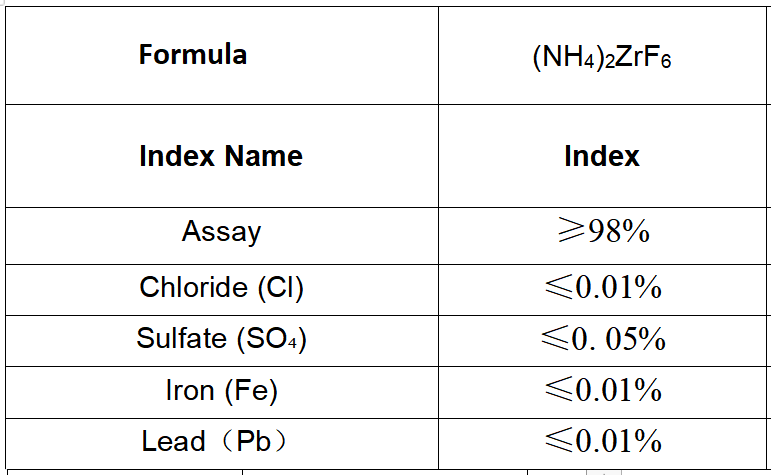
The chemical formula of Ammonium Fluorozirconate, NH4ZrF6, reflects its composition. It consists of one ammonium ion (NH4+) and one zirconium hexafluoride ion (ZrF6-). The ammonium ion is responsible for the compound’s solubility in water and its ability to form homogeneous solutions. On the other hand, the zirconium hexafluoride ion provides the compound with its unique properties, such as its high melting and boiling points.
Applications
Ammonium Fluorozirconate finds applications in various fields, most notably in the industry of metal surface treatment. It is commonly used as a flux in aluminum refining processes, where it helps remove impurities from the molten metal and improves its surface finish. Moreover, it is also used as an additive in the production of specialty glass. It aids in the elimination of bubbles and enhances the durability and clarity of the glass. Additionally, Ammonium Fluorozirconate is utilized in the synthesis of other complex zirconium compounds, which find applications in catalysts, pigments, and ceramics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ammonium Fluorozirconate is a versatile compound that has numerous applications in different industries. Its analysis can be carried out using techniques such as X-ray diffraction and infrared spectroscopy. The chemical formula NH4ZrF6 illustrates its composition, consisting of an ammonium ion and a zirconium hexafluoride ion. Its high melting and boiling points, as well as its solubility in water, contribute to its unique properties. Its primary applications include metal surface treatment and the production of specialty glass. Ultimately, this compound plays an essential role in various industrial processes, contributing to the advancement of technology and manufacturing.
Applications of Ammonium Fluorozirconate (NH4ZrF6): A Multifaceted Compound in Diverse Industries
Ammonium Fluorozirconate (NH4ZrF6) stands as a versatile and indispensable compound with a spectrum of applications across various industries. This essay explores the diverse uses of NH4ZrF6, shedding light on its significance and impact in different sectors.
Introduction:
NH4ZrF6 is derived from the reaction between zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) and hydrofluoric acid (HF), resulting in a compound with unique properties that make it valuable in various industrial processes. This compound’s stability, solubility in water, and reactivity contribute to its widespread applications.
Metal Surface Treatment and Anodizing:
NH4ZrF6 finds extensive use in metal surface treatment processes, particularly in the preparation of aluminum surfaces for anodizing. As an etchant, it removes impurities and oxides from metal surfaces, enhancing adhesion and promoting uniform anodized coatings. Treated metal surfaces exhibit improved corrosion resistance and durability, making them suitable for applications in aerospace and architectural finishes.
Electroplating:
In the field of electroplating, NH4ZrF6 is an essential component in electroplating baths for metals such as nickel and zinc. Its addition to these baths contributes to smoother and more uniform metal deposition, improving corrosion resistance and durability of plated surfaces. This application is crucial in the production of high-quality coated products used in electronics, automotive, and decorative industries.
Catalyst in Organic Synthesis:
NH4ZrF6 serves as a catalyst in various organic synthesis reactions. Its Lewis acidic properties make it a valuable tool in the production of pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, and polymers. By activating certain substrates, NH4ZrF6 facilitates more efficient and selective reactions, reducing the need for harsher reaction conditions and enhancing overall process sustainability.
Glass Etching:
NH4ZrF6 is employed in the glass industry for its ability to etch glass surfaces. As an etching agent, it selectively removes thin layers of glass, allowing for the creation of intricate designs or patterns. This controlled etching process is particularly useful in the production of decorative glassware, glass art, and electronic components.
Uranium Extraction:
In the nuclear industry, NH4ZrF6 plays a crucial role in the extraction and purification of uranium. The compound reacts with uranium compounds, forming soluble complexes that facilitate the separation and extraction of uranium. This application is vital for the production of nuclear fuel and plays a crucial role in the generation of nuclear energy.
Fluoride Production:
NH4ZrF6 is a significant source of fluoride ions. Its decomposition releases fluoride, making it valuable in the production of various fluoride derivatives. Sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride, and other fluoride salts can be derived from NH4ZrF6, finding applications in water fluoridation, metal surface treatment, and the manufacturing of specialized chemicals.
Controlling Organizations:
The regulation and safety guidelines for the use of NH4ZrF6 and other fluorine compounds are overseen by various international, national, and regional bodies. One prominent organization is the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA), collaborating with industry stakeholders, governments, and other organizations to promote responsible chemical use and safety.
For more specific information, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe play pivotal roles. These agencies provide comprehensive guidelines on the safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals, ensuring that the use of NH4ZrF6 adheres to safety and environmental standards.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Ammonium Fluorozirconate (NH4ZrF6) proves to be a crucial compound with diverse applications across different industries. From metal surface treatment and electroplating to catalysis in organic synthesis and glass etching, NH4ZrF6 plays a significant role in enhancing various industrial processes. The existence of controlling organizations ensures that its use aligns with safety and environmental standards, contributing to responsible chemical practices in the industry. As research progresses, it is likely that new applications for NH4ZrF6 will be discovered, further expanding its role in shaping the future of chemical processes and industrial applications.


