Barium fluoride
BaF2 crystal CAS NO. 7787-32-8
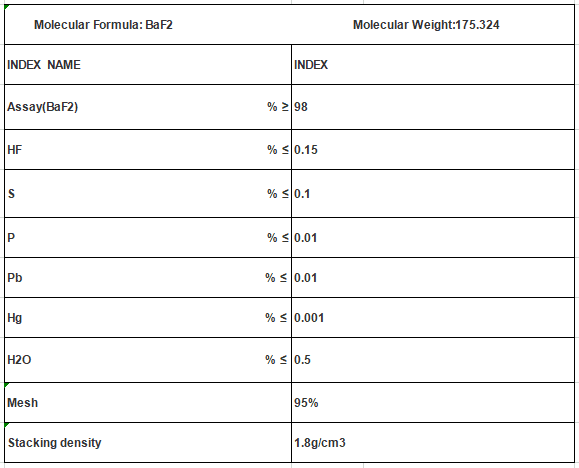
Molecular Formula: BaF2
Mol. Wt: 175.324
Cas No.: 7787-32-8
UN No.: 1564
EINECS: 232-108-0
Physical state: White cubic crystal
Relative density: 4.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)4.83
Melting point: ℃1354
Boiling point: 2260 °C(lit.)
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with acids
Regular package: 25kg per bag or according to customer’s requirements
Transportation: Dangerous goods, Hazard class: 6.1; Package group: III, UN No.: 1564
Storage: Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well
ventilated place. Keep in a dry place. Do not store in glass
It is a chemical compound that consists of barium and fluoride ions. Its chemical formula is BaF2, and it is known for its various applications in different industries. This essay will discuss the formula and applications of it.
The formula of barium fluoride, BaF2, can be broken down to understand its molecular structure. Ba indicates the presence of a barium ion, while F represents the fluoride ion. The number 2 indicates that two fluoride ions are present for every barium ion. This combination results in a crystal lattice structure, where the positive barium ions are surrounded by the negative fluoride ions, making it a stable compound.
Applications
Barium fluoride finds application in several fields due to its unique characteristics. One of its primary applications is in the field of optics. This compound has excellent transparency properties, particularly in the ultraviolet (UV) range. It is commonly used in lenses, prisms, and windows for UV spectroscopy, as well as in X-ray imaging devices. Its transparency and low refractive index make it a suitable material for these applications, providing accurate and clear readings.
Another significant application of this chemical is in the production of scintillators. Scintillators are materials that emit flashes of light when they interact with high-energy particles such as X-rays or gamma rays. This compound crystals are used in scintillation detectors as they have a high light output and fast response time. These detectors are widely used in medical imaging, nuclear physics research, and radiation monitoring.
Barium fluoride is also used in the production of ceramic materials. The addition of it to ceramics enhances their electrical and mechanical properties. It improves their resistance to cracking, thermal shocks, and chemical corrosion. Ceramics containing barium fluoride find applications in manufacturing electrical insulators, semiconductors, and high-temperature components, such as turbine blades.
Additionally
barium fluoride has applications in the field of metal production. It is used as a flux in the production of aluminum, magnesium, and other metals. The flux helps to remove impurities during the refining process, resulting in higher purity metals. It is also an essential component in the manufacture of welding electrodes, as it acts as a deoxidizer and helps prevent oxidation during the welding process.
In conclusion
barium fluoride, with the chemical formula BaF2, has numerous applications in various industries. Its transparency in the UV range makes it ideal for optical devices, while its scintillation properties make it suitable for radiation detection. In the field of ceramics and metal production, this chemical enhances material properties and acts as a flux. With its versatile applications, it continues to play a crucial role in advancing technology and various scientific fields.


