Definition
Potassium Fluozirconate (zirconium potassium fluoride), also known as K2ZrF6, is a chemical compound that belongs to the category of fluorozirconates. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. This essay will delve into the analysis, formula, and applications of Potassium Fluozirconate.
Analysis
In terms of analysis, Potassium Fluozirconate can be characterized using various spectroscopic and analytical techniques. For instance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy can be used to determine the chemical structure and composition of the compound. Additionally, X-ray diffraction analysis can provide information about the crystal structure and symmetry of the material. These analytical methods are instrumental in understanding the properties and behavior of it.
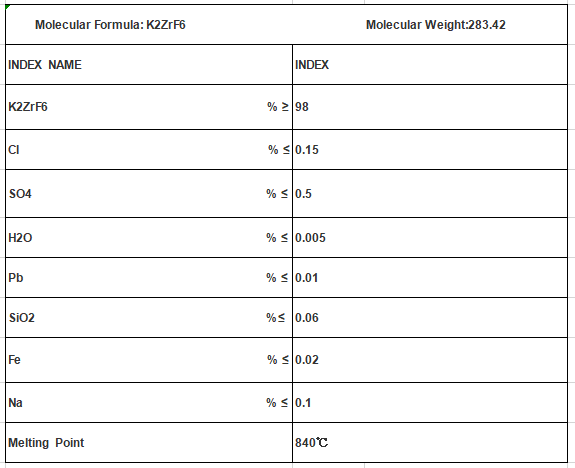
Potassium hexafluorozirconate powder CAS: 16923-95-8
Potassium fluozirconate
Molecular Formula: K2ZRF6
Mol. Wt: 283.42
Cas No.:16923-95-8
UN No.: 3288
EMS No.: F-A, S-A
EINECS: 235-186-4
The chemical formula of this compound, K2ZrF6, provides valuable information about its composition. The formula indicates that the compound consists of two potassium ions (K+) and one zirconium ion (Zr4+) complexed with six fluoride ions (F-). This formula reflects the balanced charges of the ions, ensuring electrical neutrality. The chemical formula is crucial in understanding the stoichiometry and properties of Potassium Fluozirconate.
Applications
Potassium Fluozirconate finds various applications in diverse fields. One of its primary uses is as a fluxing agent in the manufacturing of ceramic and glass materials. The compound’s ability to lower the melting point of materials makes it ideal for facilitating the formation of intricate and complex glass structures. Additionally, this compound is used in the production of metal alloys, such as stainless steel, where it acts as a deoxidizing agent. Its high reactivity with oxygen helps remove impurities and improve the quality of the metal.
Furthermore, it is also utilized in the field of dentistry. It is an essential component in dental ceramics and porcelain materials due to its ability to improve the overall strength and stability of dental restorations. The compound’s unique properties make it a preferred material in the development of dental crowns, bridges, and veneers. Its excellent biocompatibility ensures safety and durability in dental applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Potassium Fluozirconate, with its analysis, formula, and applications, has proven to be a valuable compound in several industries. Its unique properties and reactivity have made it indispensable in various manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of ceramics, alloys, and dental materials. Continuous research and exploration of Potassium Fluozirconate’s capabilities will likely reveal more applications and expand its usage across different scientific and industrial fields.
Potassium Fluozirconate (Zirconium Potassium Fluoride): Applications Across Industries
Potassium Fluozirconate, also known as Zirconium Potassium Fluoride, is a compound with diverse applications, owing to its unique properties and reactivity. This essay explores the broad spectrum of uses for Potassium Fluozirconate, emphasizing its significance and impact on various industries.
Introduction:
Potassium Fluozirconate is formed through the reaction of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) with hydrofluoric acid (HF). This compound, with its remarkable stability and solubility in water, becomes a valuable asset in multiple industrial processes.
Metal Surface Treatment:
One of the primary applications of Potassium Fluozirconate lies in metal surface treatment. Applied as an etchant, it enhances adhesion and promotes uniform coatings on aluminum surfaces, making it integral in aerospace components and architectural finishes.
Electroplating Enhancement:
Potassium Fluozirconate plays a crucial role in electroplating processes. Its addition to electroplating baths, especially for metals like nickel and zinc, contributes to smoother and more uniform metal deposition. This enhancement improves corrosion resistance and durability in industries such as electronics, automotive, and decoration.
Catalyst in Organic Synthesis:
In the realm of organic synthesis, Potassium Fluozirconate functions as a catalyst. Its Lewis acidic properties activate substrates, facilitating efficient and selective reactions. This application proves invaluable in the production of pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, and polymers.
Glass Etching Expertise:
Potassium Fluozirconate finds application in the glass industry for its superior glass etching capabilities. As an etching agent, it selectively removes thin layers of glass, enabling the creation of intricate designs in decorative glassware, glass art, and electronic components.
Uranium Extraction and Nuclear Energy:
Within the nuclear industry, Potassium Fluozirconate is instrumental in the extraction and purification of uranium. The compound reacts with uranium compounds, forming soluble complexes. This process is vital for the production of nuclear fuel, contributing significantly to the generation of nuclear energy.
Fluoride Production for Industrial Processes:
Potassium Fluozirconate is a crucial source of fluoride ions, contributing to the production of various fluoride derivatives. The decomposition of this compound releases fluoride, leading to the creation of fluoride salts. These salts, such as sodium fluoride and potassium fluoride, have applications in water treatment, metal surface treatment, and the manufacturing of specialized chemicals.
Controlling Organizations and Safety:
The use of Potassium Fluozirconate, like other fluorine compounds, is regulated by various international, national, and regional bodies. An important organization in this regard is the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA). This collaborative entity works with industry stakeholders, governments, and organizations to ensure the responsible use of chemicals.
For more detailed guidelines, regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe play essential roles. These agencies provide comprehensive information on the safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals, aligning with safety and environmental standards.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Potassium Fluozirconate (Zirconium Potassium Fluoride) emerges as a compound with versatile applications across diverse industries. From metal surface treatment and electroplating to catalysis in organic synthesis and glass etching, Potassium Fluozirconate plays a significant role in improving various industrial processes. The existence of controlling organizations ensures the responsible use of this compound, contributing to safety and environmental standards in the chemical industry. As research and development continue, Potassium Fluozirconate may unveil new applications, further solidifying its position as a crucial component in shaping the future of chemical processes and industrial applications.