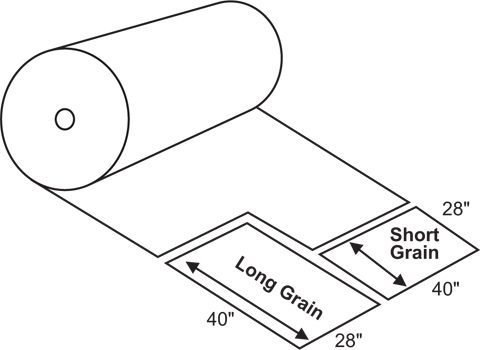
Understanding Paper Grain
Introduction
Paper quality is a crucial aspect of various industries, particularly printing and publishing. Selecting the appropriate type of paper greatly influences the final product’s durability, appearance, and performance. Among the various considerations, understanding the distinction between straight grain and cross grain paper is paramount. This essay aims to elucidate the differences between these two types of paper and their implications in professional settings.
Definition and Construction:
Straight grain and cross grain papers differ in their orientation of fibers. Straight grain paper is made with fibrous materials aligned in parallel with the grain direction, while cross grain paper utilizes fibers running perpendicular or at an angle to the grain direction. This distinction gives each type specific characteristics.
Grain Direction and Printing :
The grain direction in paper impacts various printing processes. Straight grain paper is often preferred for lithographic and offset printing methods due to its stability, reducing paper jams and image distortion. Cross grain paper, on the other hand, is more prone to curling during printing, which can affect registration and overall print quality.
Superior Folding and Creasing :
Straight grain paper excels in folding applications due to its aligned fibers, allowing for precise creasing and folding with minimal risk of cracking. Conversely, cross grain paper exhibits lesser fold strength, rendering it less suitable for intricate folding projects like brochures and pamphlets.
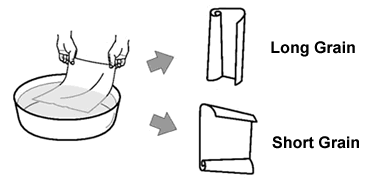
Binding and Bookmaking :
The choice of grain direction profoundly affects bookbinding techniques. Straight grain paper prevents books from warping and enhances the overall durability of bindings. Cross grain paper, however, increases the likelihood of books becoming wavy or developing uneven edges due to its less stable nature.
Durability and Aging :
Straight grain paper tends to have superior long-term durability, primarily because its fibers align with the direction of stress, making it more resistant to tearing and stretching. On the contrary, cross grain paper might suffer from structural weaknesses and frailties over time, potentially affecting its archival properties.

Environmental Factors :
Straight grain paper may be susceptible to moisture-related issues due to its parallel fiber orientation, potentially resulting in warping and expansion. Cross grain paper, with its perpendicular fibers, offers better dimensional stability and is less prone to moisture-related deformations.
Packaging and Strength Considerations :
Typically, straight grain paper is preferred for packaging applications due to its strength and resistance to tearing. It provides stability and prevents damage to the contents within. Cross grain paper, while capable of withstanding moderate force, may not be as robust, making it less suited for demanding packaging requirements.
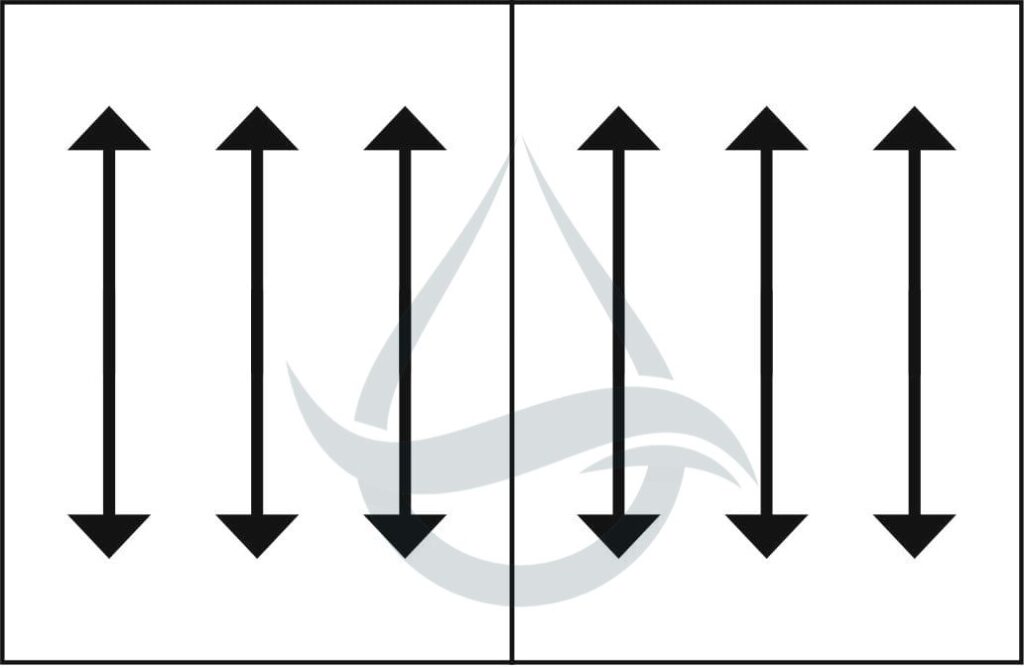

Availability and Cost Considerations :
Straight grain paper is widely available and more commonly used, making it generally more affordable and easier to procure. However, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of individual projects when comparing costs, as certain applications may necessitate cross grain paper’s unique characteristics.
Artistic and Creative Applications :
Cross grain paper is often favored in creative endeavors such as sketching, drawing, and water coloring due to its enhanced texture and ability to hold more ink or pigment. The structure of cross grain paper provides a unique artistic experience and is often sought after by artists for its distinct visual appeal.
Conclusion :
Understanding the differences between straight grain and cross grain paper is essential for professionals in the printing and publishing industries. The choice between the two depends on specific application requirements such as printing techniques, folding demands, bookbinding, durability, environmental factors, packaging needs, cost considerations, and artistic ventures. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of these aspects allows for informed decision-making, leading to enhanced product quality and customer satisfaction.